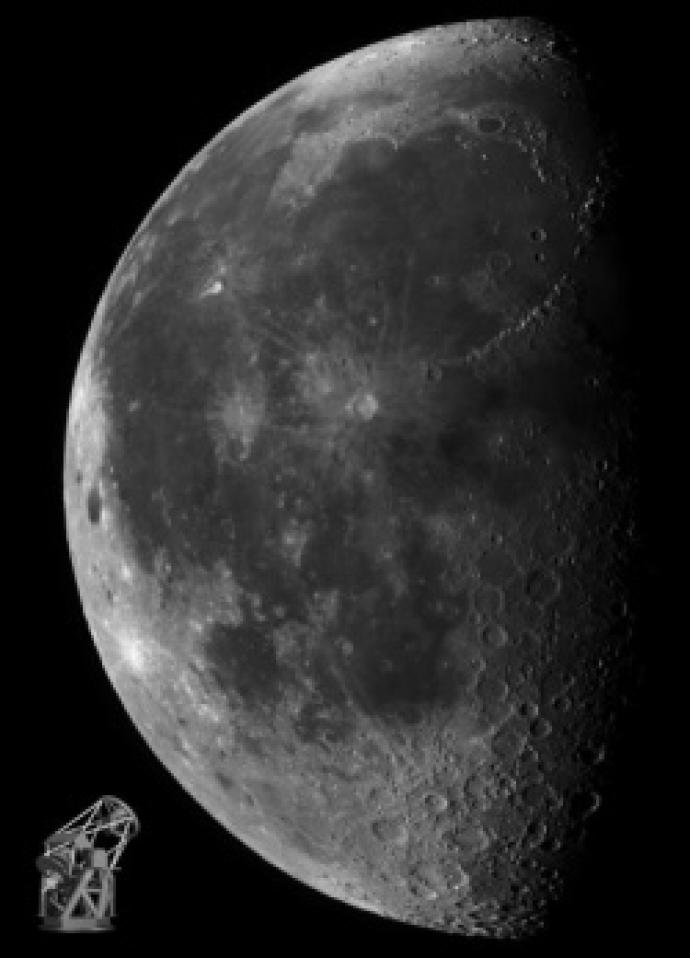
The Moon
The Moon is the largest and brightest object we see in the night sky.

Earth
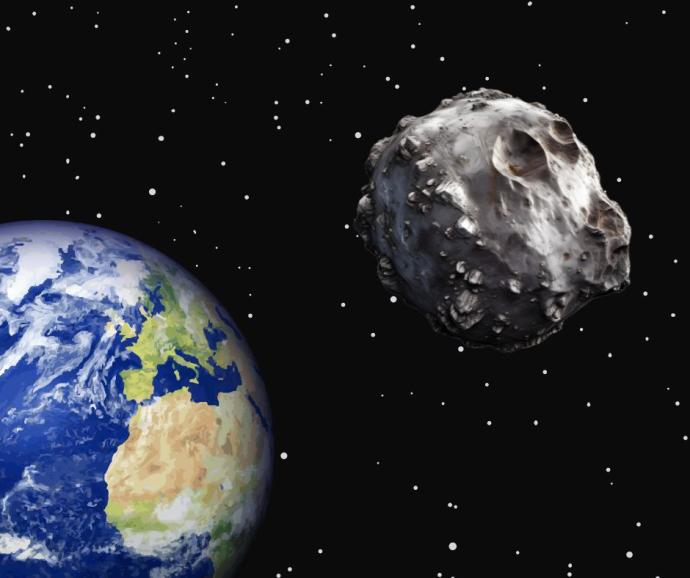
Near-Earth Objects

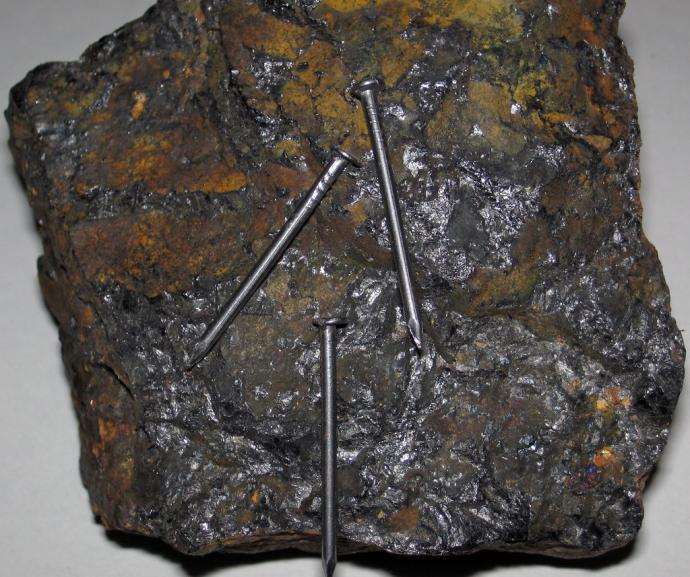
Magnetism
Since ancient times, people have known about some rocks that could attract iron. When these rocks were rubbed on other types of metal, they had the power to make them attractive too. These items could also push each other away, repelling each other.

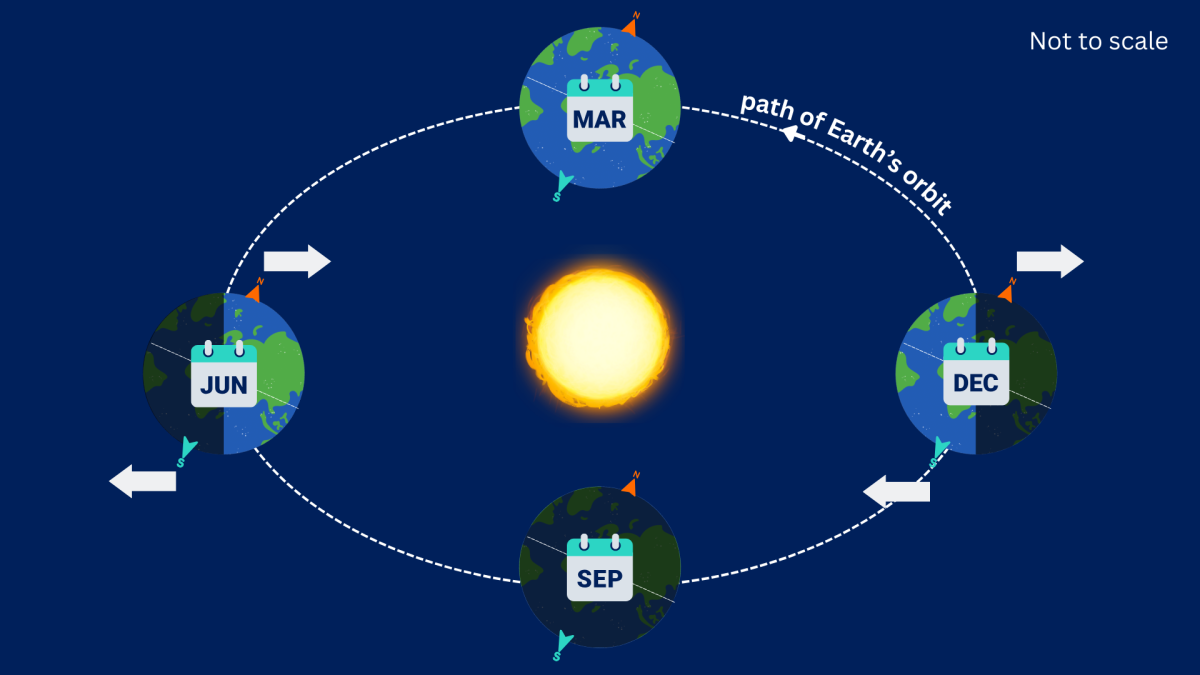
Seasons
There are four seasons: Spring, Summer, Autumn and Winter. Parts of the Earth experience each season once each year.
Life on Earth
Planet Earth was formed around 4.5 billion years ago. The first signs of life began about 3.6 billion years ago, in the ocean. The water in the ocean protected organisms living there from the dangerous rays of the sun.

Eclipses
An eclipse is when objects in space line up. One object moves into the shadow of the other.

Sky Coordinates
We use coordinate systems to find the position of a point on a surface.
For example, Latitude and Longitude are used to locate a position on the Earth's surface. They are both measured as angles.

Stargazing Glossary
Welcome to our stargazing glossary!
Here, you'll find key terms that will help you better understand the wonders of the night sky.

