Nuclear physics is the branch of science which looks inside atoms. It looks at the nucleus, and what effect different interactions have on it.
These interactions come in 2 main forms: nuclear fission and nuclear fusion.
Nuclear fission is where the nucleus breaks apart into smaller pieces.
Nuclear fusion is where the nucleus gets bigger by fusing, or 'gluing', with another nucleus. Both of these release energy.
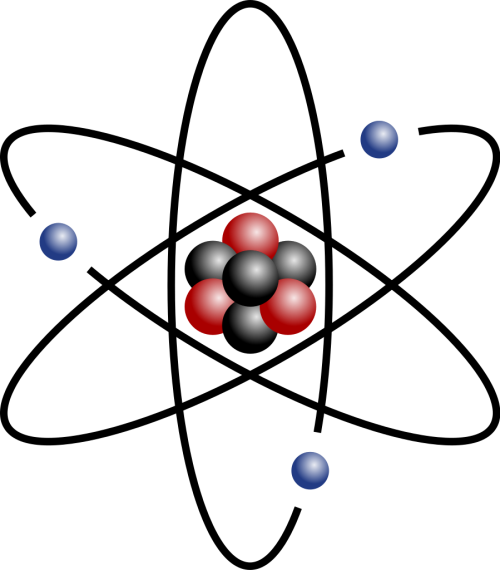
A nucleus sits at the centre of an atom. It was only found in 1911 by New Zealand physicist Ernest Rutherford. The nucleus contains 2 types of particles known as neutrons and protons.
The proton has a positive electric charge. The neutron has no charge at all. Between them, they make up most of the mass of an atom as the surrounding electrons are tiny in comparison.
The nucleus has a huge impact on the Universe we see. All the stars we see are powered by nuclear fusion. It is the fusion of nuclei which gives the star energy, and light.
- Nuclear fusion
The light and heat from stars is made by a process called nuclear fusion.
Fusion happens when 2 atoms are forced together to form a heavier atom. This creates a lot of energy. However, fusion can only occur at the incredibly high temperatures and pressures found in the centre of stars.
All the elements in the Universe heavier than hydrogen and helium were made in stars through nuclear fusion. When the star dies these elements are then emitted into space. They move into nearby gas clouds, or nebula, and form the building blocks for a new generation of stars.
Our Sun and all the planets in the Solar System, contain these elements. Elements produced inside the very first stars. This means that you, and everything around you, is also made of "stardust".
Scientists on Earth are trying to find a way to make nuclear fusion power stations. These would be much cleaner than current nuclear fission power stations. They would also produce a lot of energy. But it is really hard to do on Earth because you have to make conditions like we have inside stars. You need to make the gas in the machines very hot and with a high pressure.
Image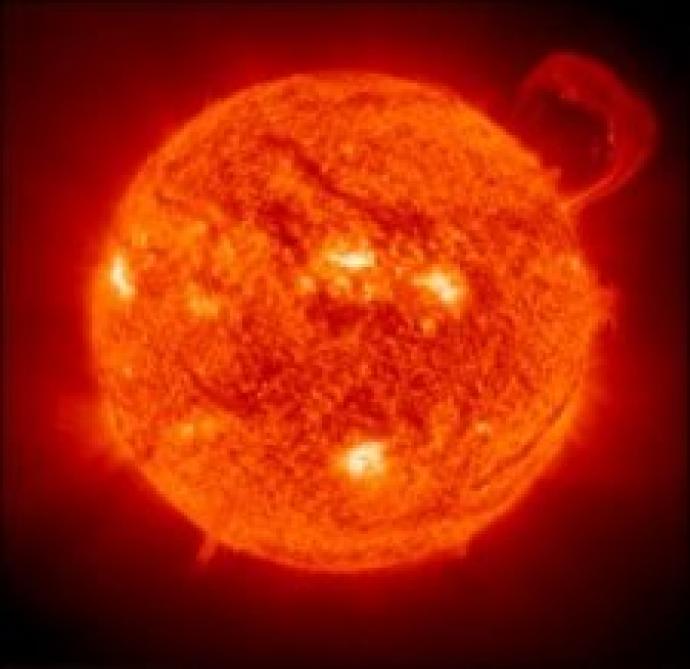 CreditThis work by ESA/NASA/SOHO is licensed under Creative Commons Zero v1.0 Universal
CreditThis work by ESA/NASA/SOHO is licensed under Creative Commons Zero v1.0 UniversalNuclear fusion occurs in stars
