A galaxy is a large collection of stars, dust and gas. They are surrounded by dark matter, and are held together by gravity. It is thought that there are around 100 billion (100,000,000,000) galaxies in the Universe.
Galaxies come in all shapes and sizes. The smallest galaxies, known as dwarfs, contain just a few million stars. The largest giant galaxies can contain around 1 trillion stars - that's an incredible 1,000,000,000,000 stars. Scientists have estimated that there are at least 100 stars in space for every grain of sand on Earth's beaches!
It is thought that super-massive black holes live at the centre of most galaxies. This includes our galaxy (the Milky Way). Astronomers have found it by looking at the movement of stars close to the centre of the galaxy.

- The Milky Way
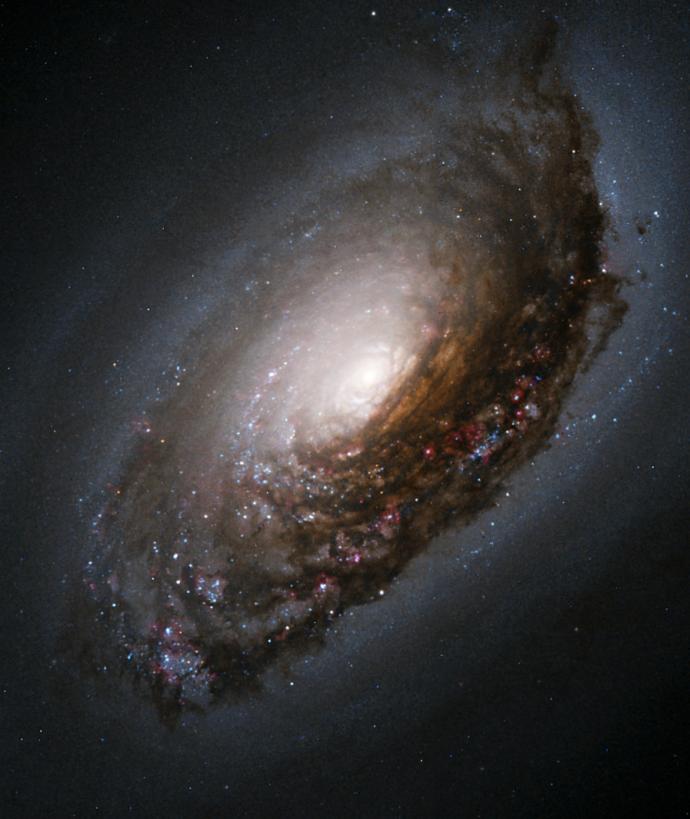
Our own galaxy is called the Milky Way. It is a large spiral galaxy. Our Solar System sits towards the edge it, about 26,000 light-years from the centre. The closest star to our Solar System is Alpha Centauri, which is just 4.4 light-years away.
As we live inside the Milky Way galaxy, it is hard to see its shape. From Earth, we see a faint, white band stretching across the night sky. The name of our galaxy comes from the Latin words meaning "milky path".
Image CreditThis work by Juliancolton is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 4.0 International
CreditThis work by Juliancolton is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 4.0 InternationalPanorama of the Milky Way over Bontecou Lake in Dutchess County, New York Looking closely at this band, we see that it is made up of billions of stars. A lot of the light coming from those stars is blocked by gas and dust in the galaxy. It is this gas and dust which will ultimately form new stars.
ImageCreditThis work by Georgia Hurst is licensed under All rights reservedA closer view of the Milky Way band Telescopes have accurately measured the positions of stars and found that the Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy. It has over 200,000,000,000 (200 billion) stars inside it. It is disk shaped with a bulge in the middle. The Milky Way is about 100,000 light-years across and 1000 light-years thick.
The Sun is on one of the spiral arms of the Milky Way, two-thirds of the way out from the centre.
Image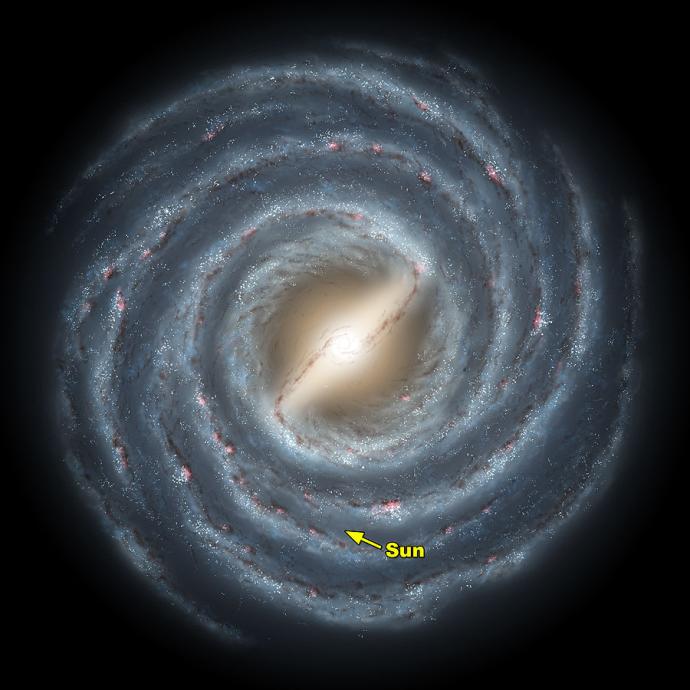 CreditThis work by NASA is licensed under Creative Commons Zero v1.0 Universal
CreditThis work by NASA is licensed under Creative Commons Zero v1.0 UniversalIn the same way that the Earth orbits the Sun, the Sun orbits the centre of the Milky Way. It travels at a speed of almost 220 km/s. Even at this speed it takes our Sun around 225 million years to complete one full orbit of the galaxy.
- Quasars
A Quasar is an energetic object in space that looks like a star. They are actually galaxies, very far away, with very bright cores in the middle.
They are probably the brightest objects in the whole Universe, many times brighter than normal galaxies. A quasar can be as bright as 1,000 Milky Way galaxies!
Image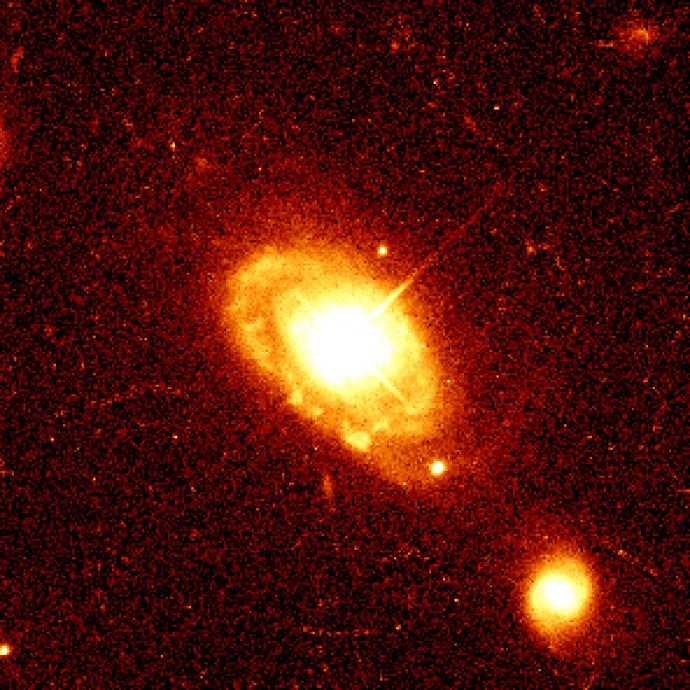 CreditThis work by John Bahcall (Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton)/Mike Disney (University of Wales)/NASA/ESA is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International
CreditThis work by John Bahcall (Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton)/Mike Disney (University of Wales)/NASA/ESA is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 InternationalQuasar PG 0052+251 Astronomers think that quasars are powered by supermassive black holes found at the centre of most galaxies. The power from a quasar comes from material crashing together at enormous speeds. This is because the material is being pulled into the black hole and swirling around.
The material comes from stars which have got too close to the black hole. The gravity from the black hole is so strong that it pulls the stars apart. This makes a string of huge explosions that can be seen across the Universe. The furthest quasar we can see is more than 13 billion light years away!
- Galaxy Clusters
Gravity is powerful in space. It allows planets to orbit stars, and stars to orbit around galaxies. It also brings galaxies together. There are many groups, and clusters of galaxies in space that are bound to each other by gravity.
Galaxy groups have less than 50 galaxies and are 3 to 7 million light-years across. The mass can be 10,000,000,000,000 (10 trillion) times that of the Sun. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group of galaxies, which has around 40 members.
Galaxy clusters are even bigger. They can have between 50 and 1,000 galaxies. Reaching 7 to 35 million light-years across, clusters can contain 10 to 100 times more mass than galaxy groups.
If you were to look at a cluster for a very long time, you would see that the galaxies in it were all swarming around a central point.
Image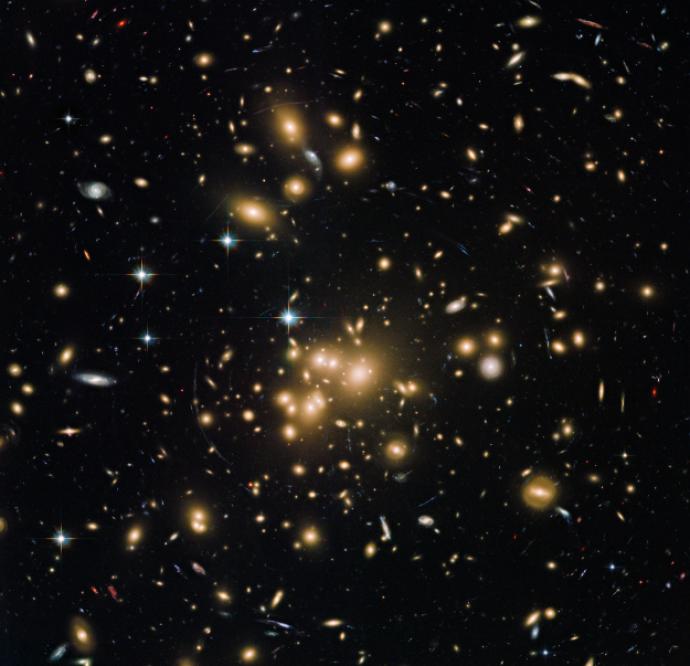 CreditThis work by NASA/Hubble is licensed under Creative Commons Zero v1.0 Universal
CreditThis work by NASA/Hubble is licensed under Creative Commons Zero v1.0 UniversalThe cluster Abell 1689
