An eclipse is when objects in space line up. One object moves into the shadow of the other.
An example would be if we were on the Moon looking back at Earth. Each day the International Space Station would pass in front of the Earth 15 times. When it did, it would eclipse the Earth.

Eclipses don’t have to be ‘total’ (an occultation) – when the passing object fully hides the more distant one. They can be transits, where only part of the more distant object is hidden.
When 3 objects in space line up in this way, we call it a syzygy.
We commonly think of eclipses when the Earth, Sun and Moon align. This can make a solar or lunar eclipse. But in space this happens all the time with more distance objects too.
- A Solar Eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Earth moves through the shadow cast by the Moon. The sky gets dark, like at night-time!
It is dangerous to look straight at the Sun. Even during an eclipse it is bright enough to damage your eyes. It could even blind you! Download the Solar Eclipse Guide (PDF) for safety tips on observing an eclipse. The guide was created by Royal Astronomical Society and the Society for Popular Astronomy.
The Moon is smaller than the Sun so how does it cause an eclipse? Well, the Moon is 400 times smaller than the Sun, but it's 400 times closer. This quirk of nature means the Moon and the Sun look the same size in the sky.
There are three types of solar eclipse:
- Total solar eclipse
- Partial solar eclipse
- Annular eclipse
Image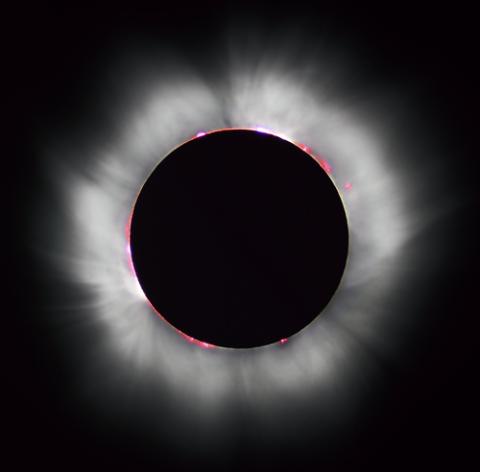 CreditThis work by Luc Viatour is licensed under GNU General Public License v2.0 or later
CreditThis work by Luc Viatour is licensed under GNU General Public License v2.0 or laterTotal Solar Eclipse from France, 1999. - Total Solar Eclipse
During a total solar eclipse the Moon completely covers the Sun. For this to happen, the Earth, Moon, and Sun have to be in a straight line.
The Moon takes 27.3 days to orbit the Earth. So why isn't there a total solar eclipse every month?
The Moon's orbit is on a tilt compared to the Earth's orbit of the Sun. It usually passes above or below the line between the Sun and the Earth. The times when all three objects line up, that's when we get a solar eclipse.
A total solar eclipse only lasts for a few minutes. This is because the Moon's shadow moves at 1,700 kilometres per hour!
A total solar eclipse occurs on Earth roughly every 18 months. But the Moon's shadow only covers a part of the Earth's surface. So you have to be in the right place to experience a solar eclipse. And you have to wait 300 - 400 years to experience an eclipse in the same place twice!
Discover where in the world an eclipse will next take place.
- Partial Solar Eclipse
A partial solar eclipse happens when parts of the Earth not completely in the Moon's shadow. The Sun looks like it has a dark shadow on part of its surface. The sky gets darker, but it doesn't feel like night-time.
Image CreditThis work by The Schools' Observatory is licensed under All rights reserved
CreditThis work by The Schools' Observatory is licensed under All rights reservedWhen the Earth Moon and Sun are in a straight line we get solar eclipses - Annular eclipse
The Moon isn't always at the same distance from the Earth. When it's a bit further away, it doesn't look as big in the sky.
This means it can't cover the Sun completely. We can still see a ring of the Sun around the Moon. This is called an annular eclipse.
- A Lunar Eclipse
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves through the shadow cast by the Earth.
It's safe to look at a lunar eclipse. Although the Moon is in the Earth's shadow, some sunlight reaches it. (It's the Sun's light reflecting off its surface which makes the Moon shine). This light has passed through the Earth's atmosphere, which removed the bluest light. This is why the Moon looks a red-brown colour during an eclipse. Lunar eclipses last up to 4 hours! This is because the Earth's shadow is bigger than the Moon.
A lunar eclipse only happens at full moon. This is when the Moon and Sun are on opposite sides of the Earth. Our diagram shows what happens during a lunar eclipse. There are two types of lunar eclipse:
- Total lunar eclipse
- Partial lunar eclipse.
We call the darkest part of the shadow, the 'umbra'. It is the dark cone-shaped shadow in the diagram. A total lunar eclipse is when the whole Moon is in this part of the shadow. During a partial lunar eclipse, only part of the Moon is.
Image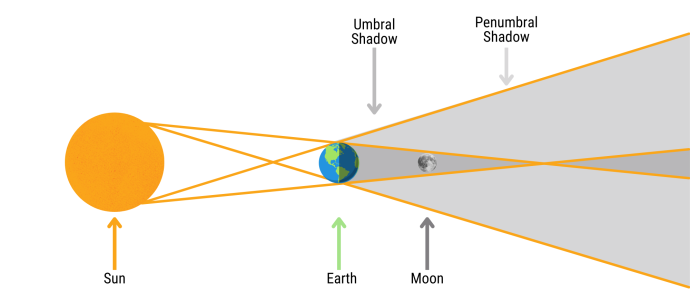 CreditThis work by The Schools' Observatory is licensed under All rights reserved
CreditThis work by The Schools' Observatory is licensed under All rights reservedThe geometry of a lunar eclipse
