Stars are massive, glowing balls of extremely hot gas (called plasma) in space. The Sun is our closest star.
Although stars look small in the sky, they are actually massive objects, millions of times larger than the Earth. They look small because they are very far away.
After the Sun, the nearest star is Proxima Centauri. It is 4.3 light years away, which is about 41 million, million km away!
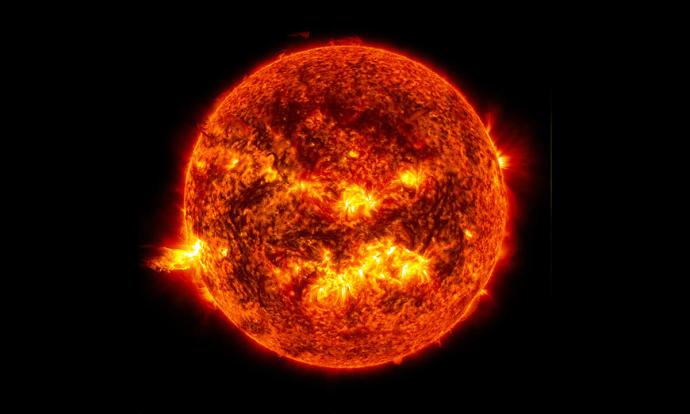
In astronomy, we measure the brightness of stars in different ways. We often use the word 'luminosity' when talking about how brightly something glows.
All stars are formed inside a nebula, but they come in lots of different sizes and colours. These differences can tell us a lot about what type of star they are.
Stars shine for many millions of years, but do not last for ever. After forming, they go through several stages which we call the life cycle of a star.
