The Earth's atmosphere is vital for life. But did you know it can cause problems for astronomers.
Some kinds of light can not get through the atmosphere at all! So when astronomers build a new professional telescope, they choose a place which minimises the problems caused by the air.

- Light Pollution
Have you ever noticed you can see more stars from the countryside than from a town? This is probably due to light pollution.
Light pollution is what we call too much artificial light which escapes up into the night sky. It creates a hazy orange glow that can obscure our view of the stars. This is why it is also known as sky-glow. Light pollution is caused by things like street lights, advertising boards, and building lights in urban areas.
Effects of Light Pollution
It is important to have street lights for our own safety. But poorly designed and misdirected street lights have increased the amounts of light pollution across the world. This is bad news for:
- Stargazers: as it becomes hard to see stars and planets.
- Wildlife: Many animals need natural light to survive. Light pollution can change how they find food, reproduce, and move from place to place.
- Environment: Too much artificial light uses more energy, increasing carbon dioxide that pump into the atmosphere each year.
Reducing Light Pollution
The good news is that light pollution can be reduced. If we minimise the amount of light that escapes into the night sky, it will improve our view of the stars and help wildlife and environment. Here are some ways to reduce light pollution:
- Switch off lights when you don't need them.
- Choose bulbs that aren't too bright.
There are still many parts of the UK that allow us to see the night sky in its full glory. These tend to be the more remote areas. Have a look at the list of UK and Ireland Stargazing Sites. You can also use this map to see the amount of light pollution in England. It was created by the 'Earth Observation Group' at the NOAA National Centres for Environment Information.
Image CreditThis work by National Optical-Infrared Astronomy Research Laboratory (NOIRLab). is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International
CreditThis work by National Optical-Infrared Astronomy Research Laboratory (NOIRLab). is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 InternationalInfographic Illustrating the Impact of Light Pollution on Our Ability to See Stars and Other Objects in the Night - Astronomical Seeing
The atmosphere acts a bit like a "frosted" glass window. Images of stars and galaxies can look blurred and fuzzy. Astronomers call this effect, seeing. The seeing is also why stars look like they "twinkle".
The worse the seeing, the more they blur. It is changes in the Earth's atmosphere which causes the seeing conditions. The less steady the atmosphere, the worse the seeing becomes.
Effects of Astronomical Seeing
If the seeing conditions are poor, we do not see as much detail in telescope observations. It is like looking into the sea on a windy day. The more waves in the water, the less you see beneath the surface. If the seeing conditions are good, it's like looking into a flat calm sea. You can clearly see objects in more detail.
A clear night sky may look calm but there can still be movement in the air. There are up-drafts and turbulent layers which affect the light passing through it. These can cause the quality of images to change rapidly.
Reducing Astronomical Seeing
All observatories based on Earth are affected by seeing. We can reduce the negative effects by:
- Putting telescopes on the top of high mountains. This means the telescopes can look through less atmosphere.
- Astronomers have also developed something called adaptive optics technology. This corrects for the effect of seeing.
- There is one way to completely remove the effects of seeing. Launch your telescope into orbit above the Earth's atmosphere.
Video fileCreditThis work by The Schools' Observatory is licensed under All rights reservedVariations in Seeing on Star and Moon - Weather
It is almost impossible to see the night sky through thick cloud! That is, unless you are doing radio astronomy.
Radio telescopes can 'see' through cloud because radio waves can travel through it.
Radio telescopes (like the SKA) are usually built away from electrical noise and radio transmissions. These can interfere with the radio light from space.
Some telescopes have even been launched into space. This avoids all problems caused by the Earth's atmosphere.
Image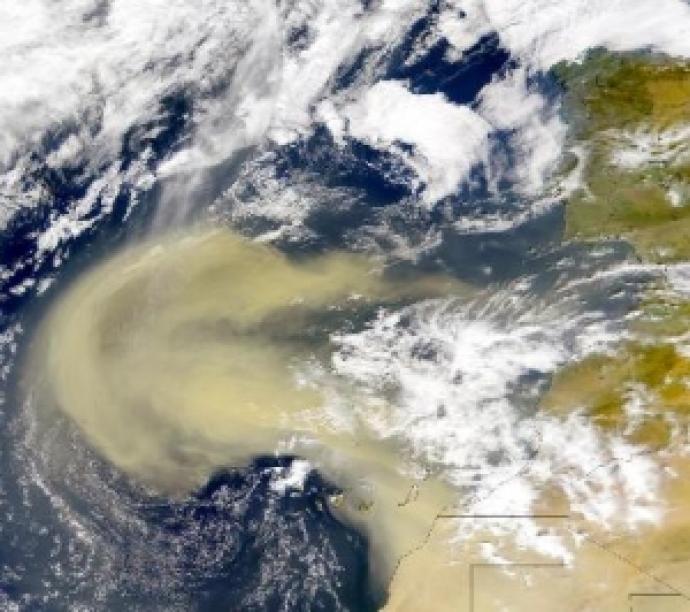 CreditThis work by SeaWiFS Project, NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, ORBIMAGE is licensed under Creative Commons Zero v1.0 Universal
CreditThis work by SeaWiFS Project, NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, ORBIMAGE is licensed under Creative Commons Zero v1.0 UniversalA dust storm over the Canary Islands - Transmission
The amount of light that gets through the atmosphere is called the transmission of the atmosphere. The less air we look through the more we can see. So it is better to do astronomy at high altitudes or from space!
Professional astronomers usually put their telescopes on high mountains above most of the clouds. They are also often in remote areas, well away from towns and cities. Often, the best place is on an island. The sea keeps the atmosphere more stable, so there is less blurring.
This is why the Liverpool Telescope is on a mountain in the island of La Palma!
